The circadian rhythms.
What are circadian rhythms?
These are physical, mental, and behavioral changes that follow a 24-hour cycle and which respond mainly to light and dark, and affect most living beings, including animals, plants, and microbes, being part of a natural process.
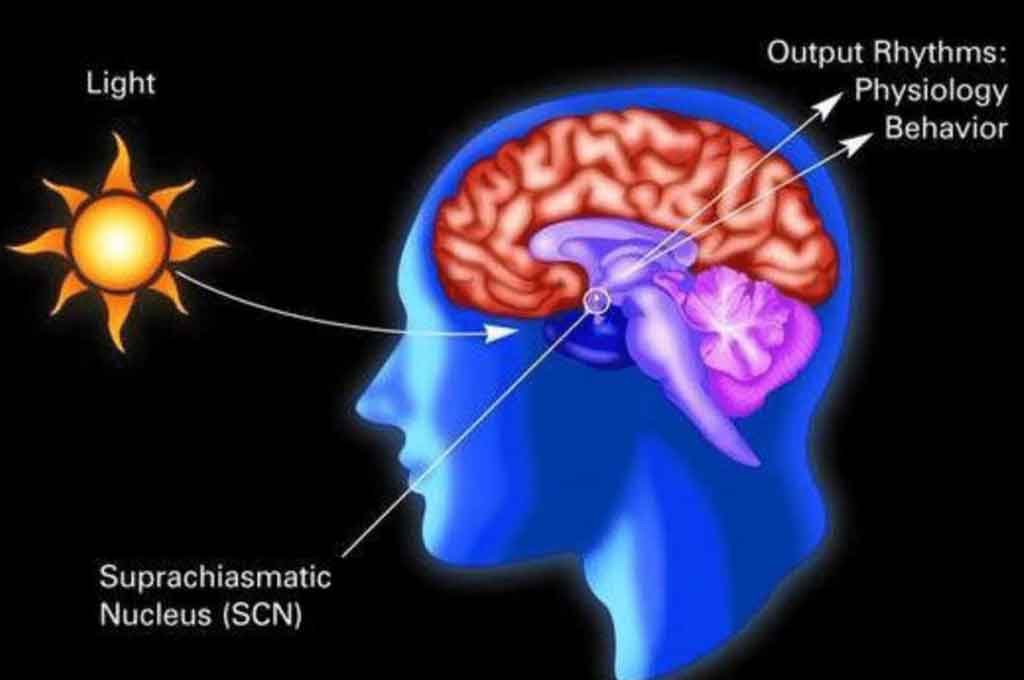
Those responsible for regulating circadian rhythms are biological clocks, which are the natural time devices of an organism and are composed of proteins that interact with cells throughout the body; the main biological clock is the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus (SCN) and it is found in the brain located in the hypothalamus.
The SCN controls the production of melatonin, a hormone that produces drowsiness, it receives information about the incoming light from the optic nerves, which transmit it from the eyes to the brain and when there is less light, the SCN tells the brain to make more melatonin to make you sleepy.
Influence of circadian rhythms.
Circadian rhythms can influence important body functions, such as:
- In the release of hormones,
- In eating habits and digestion,
- And in body temperature.
Factors that change circadian rhythms.
Changes in the body and environmental factors can cause circadian rhythms and the natural light-dark cycle to be out of sync; for example:
- Mutations or changes in certain genes can affect biological clocks.
- Jet lag or shift work changes the light-dark cycle.
- Light from electronic devices at night can confuse biological clocks.
These changes can cause sleep disturbances and lead to other chronic medical conditions, such as obesity, diabetes, depression, bipolar disorder, and seasonal affective disorder.
The understanding and study of circadian rhythms or biological clocks are of great importance because the human body is better known and helps to have better treatments for chronic medical conditions.



Comentarios
Publicar un comentario